++ 50 ++ c g base pair 137404-What is the base pair in dna
DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter either A, T, C, or G Chargaff's rules state that DNA from any species of any organism should have a 11 protein stoichiometry ratio (base pair rule) of purine and pyrimidine bases (ie, AT=GC) and, more specifically, that the amount of guanine should be equal toA green solvent Quantitative thermodynamic analyses shows that A–T base pairs are more stable than G–C base pairs in the hydrated ionic‐liquid choline dihydrogenphosphate because of specific interactions between DNA bases and choline ionsIn normal DNA, A will pair with T across the double helix and C will pair with G More importantly, the nucleotides mispair (eg C sits across from T) at extremely low frequency, which underlies the ability for DNA to store information, replicate that information during cell division, and to copy that information into RNA
28 3 Base Pairing In Dna The Watson Crick Model Chemistry Libretexts
What is the base pair in dna
What is the base pair in dna-C) Now assume gene Y was mutated such that only the base pair found at position 2100 was changed from a C/G to an A/T Transcription and translation of gene Y still occur • Would the first transcript be the same length, shorter or longer than the first transcript produced fromThe WatsonCrick basepair (C·G) is the most stable of the four, with the highest melting temperature, of 605 ºC All mismatches are destabilized by a significant amount relative to it, with significantly lower melting temperatures The C·C mispair is the least stable, with a depression in T m of 173 ºC The destabilizing effect of


Molecular Genetics High School Biology Science Khan Academy
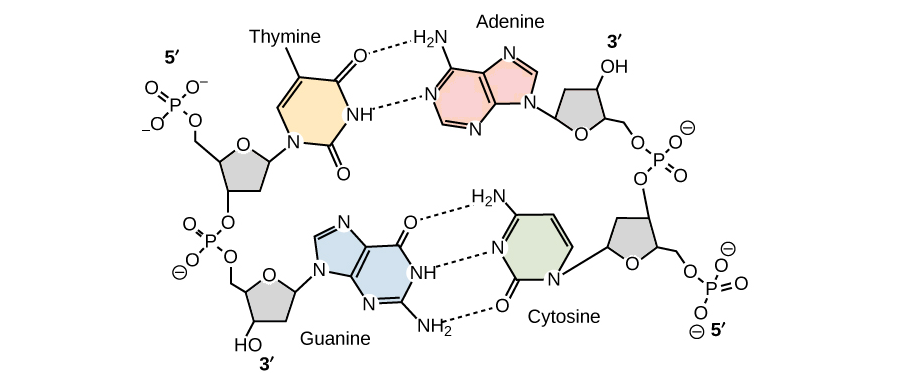
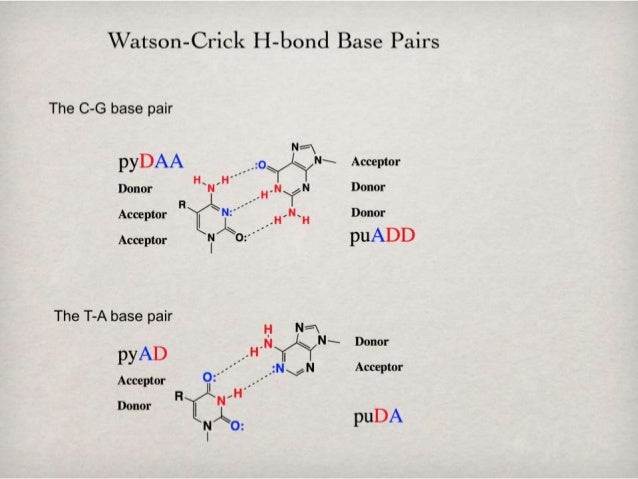
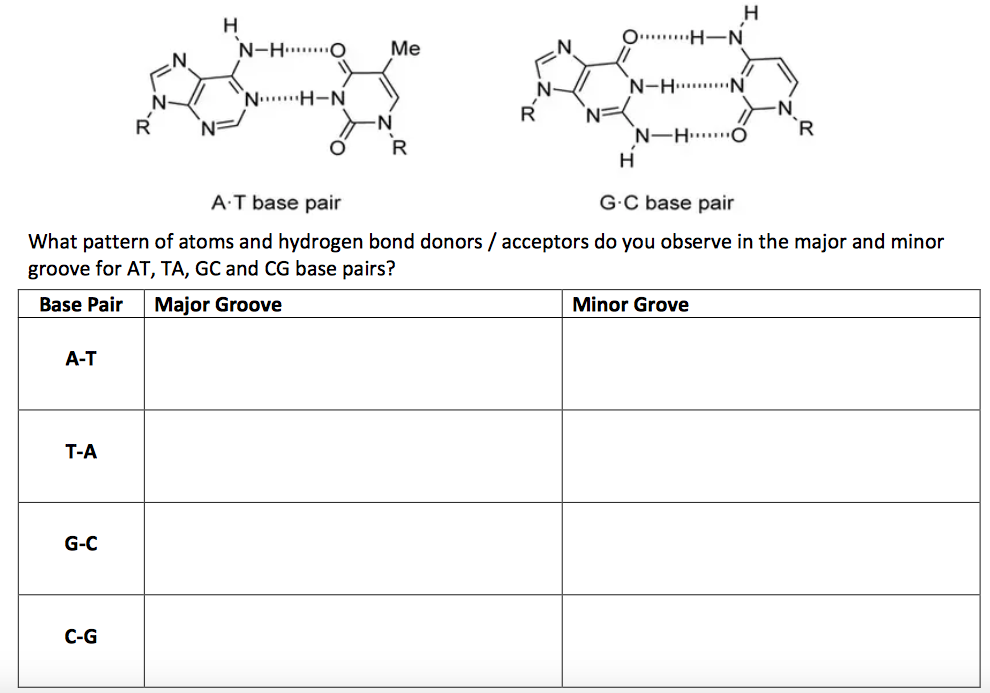
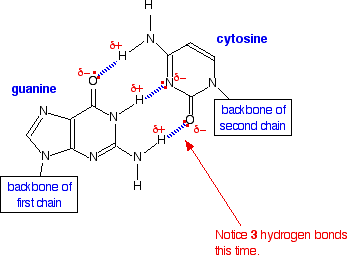
The base pairing of opposite strands is stereochemically selective, Adenine always pairing with Thymine, and Guanine with Cytosine Two and three hydrogen bonds are formed in AT and GC base pairs, respectively AT and GC base pairing results in strand complementarity, with one strand of the double helix forming a sequence of basesIndeed, cis G& A pairs with two hydrogen bonds between the Watson–Crick sites of both bases and a distance between the C1′ atoms larger than those in Watson–Crick pairs (126 Å instead of 105 Å) occur in tRNA structuresVisit Studycom for thousands more videos like this one You'll get full access to our interactive quizzes and transcripts and can find out how to use our vi
A T G G C T A C Knowing the base pairing convention of A always pairing with T and G always pairing with C makes the complementary strand of the molecule understood It is this feature of complementary base pairing that insures an exact duplicate of each DNA molecule will be passed to its daughter cells when a cell dividesA G = T C or (A G) / (T C) = 1 Chargaff's parity rule 2 This states that the percentage content of any nucleotide is the same across both strands, ie the percentage of A/G/C/T is the same on both strands of DNA It also states that the ratio of the two base pair units remains constant across a species (A T) (G CThe strength of hydrogen bonding between
A does not pair with G because the two large bases are too big to fit inside the Å circle A TC pair has plenty of room to fit into the Å circle, but the bases are too far apart to be stabilized by hydrogen bonds across the helical axis Only a pairing between a single and a doubleringed base has the proper size to fit into the doubleAnswer Save 4 Answers Relevance Asst Prof Lv 7 1 decade ago Favorite Answer Since the AT pair is held together by 2 hydrogen bonds, and the CG pair is held together by 3 hydrogen bonds, I would think that the CG pairbond is stronger, justChargaff's rule, also known as the complementary base pairing rule, states that DNA base pairs are always adenine with thymine (AT) and cytosine with guanine (CG) A purine always pairs with a pyrimidine and vice versa However, A doesn't pair with C, despite that being a purine and a pyrimidine


Astronauts In Structure Space



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
K = G or T = Keto M = A or C = aMino S = G or C = Strong base pair W = A or T = Weak base pair double base codes D = Asp = Aspartic acid E = Glu = Glutamic acid K = Lys = Lysine Q = Gln = Glutamine W = Trp = Tryptophan (big letter big residue) nonobvious codes (you just have to learn them!) B = not A (G or C or T) D = not C (A or G or T) HAdenine (A) is always supposed to pair with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) is always supposed to pair with guanine (G) The two "WatsonCrick" base pairs, AT and CG, form the DNA sequences of all life as we know it However, if G were to somehow mispair with T, for example, that would be a mutationThe G·U wobble base pair is a fundamental unit of RNA secondary structure that is present in nearly every class of RNA from organisms of all three phylogenetic domains It has comparable thermodynamic stability to Watson–Crick base pairs and is nearly isomorphic to them Therefore, it often substitutes for G·C or A·U base pairs


Watson Crick Base Pairs Character And Recognition Of Chemical Biology


Naflex Nucleic Acids Flexibility
Following video illustratres how different edges of Guanine are bonded when involved in either a canonical GC pair, or a socalled sheared GA Glycosidic Bond Orientation A glycosidic bond joins the sugar, ribose, and the base in a nucleotideThe glycosidic bonds of the two bases in a base pair can be oriented in the same (cis) or opposing (trans) directionsAmong the four DNA nucleosides, C, A, and G contain exocyclic amines that are prone to deamination, as opposed to thymidine that lacks this group C and A, when deaminated, cause a reversal of polarity of base hydrogenbonding surfaces and cause U to pair with A and I with C But xanthosine (deaminated G) prefers to base pair with C aloneThe nonWatson–Crick type of base pairing also comprises the base pairs formed by inosine (I) with C, T, or A, purine base pairs A · G (or I), A · A, and G · C, and the reverse Watson–Crick base pair A · T In the reverse Watson–Crick A · T pairing, the T ring is rotated 180° around the N3C6 axis from the normal Watson–Crick pair


Base Pair Eterna Wiki


Q Tbn And9gctfmfjn8q4hhz3c Ovwd6wke3wm7 Bfkjo5rk8mosy6arj8ls0 Usqp Cau
CG because there are 3 hydrogen bonds?NonWatsonCrick basepairing models display alternative hydrogenbonding patterns;In doublehelical DNAs, the most stable Watson–Crick (WC) base pair (bp) can be in thermal equilibrium with much less abundant Hoogsteen (HG) bp by the spontaneous rotation of the glycosidic angle in purine bases Previous experimental studies showed that in the case of a G·C bp, the population of the transient HG is enhanced as a protonated form (HG) through the protonation of the



Better Base Editing In Plants The Scientist Magazine



Chemical Structures Of A T A U B C G C C L G C And D Q C G Download Scientific Diagram
G↔C, A↔T • A and G are purines (double‐ring), C and T are pyrimidines (single‐ring) DNA to mRNA • Possible Bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil (RNA only) • G↔C, A→U, T→A • A and G are purines (double‐ring), C, T, and U are pyrimidines (single‐ring) mRNA to tRNA •Qualitatively, guanine (G) and cytosine (C) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (A) bonds specifically with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA Quantitatively, each GC base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while AT and AU base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds To emphasize this difference, the base pairings are often represented as "G≡C" versus "A=T" or "A=U"Incorporating mismatched A/C or G/T base pairs did not noticeably affect the conformations of the duplexes in 115 mM Na but resulted in perturbed BZ conformations at 45 M Na For any mismatched base pair duplex, the BDNA domain of the hybrid BZ structure formed at 45 M Na is significantly perturbed while the ZDNA domain is less



Base Pairs


N Ho Me N H N N R N R N N H O R O R A T Base Pai Chegg Com
The answer is that AT and GC pairs maximize the number of hydrogen bonds across the shared helical axis A's hydrogen donors can pair up with T's hydrogen bond acceptors, and G's hydrogen bond acceptors can pair up with C's hydrogen bond donors AT and GC are called complementary base pairsWhat researchers have done is to create a new pair of bases that adds a third type of base pair to the existing AT and CG base pairs This new can exist in a normal DNA double helix without significantly disrupting its structure This in theory allows the DNA to store more information because the DNA now encodes six bits (A,T,G,C,X,Y) insteadC with G the pyrimidine cytosine (C) always pairs with the purine guanine (G) This is consistent with there not being enough space ( Å) for two purines to fit within the helix and too much space for two pyrimidines to get close enough to each other to form hydrogen bonds between them But why not A with C and G with T?


Base Pair Wikipedia



Figure 1 From Synthetic Receptors For Cg Base Pairs Semantic Scholar
An A always pairs with a T, and a C always with a G The human genome contains approximately 3 billion of these base pairs, which reside in the 23 pairs of chromosomes within the nucleus of all our cellsBases pair in a certain way because of how the protons and electrons in their atoms are arranged Base pairing requires some amount of energy, and the easiest, most energyefficient pairs to form are the "right" ones—AT and CG In effect, the GT pair has to overcome an energy barrier to form and maintain itselfAccording to Chargaff rule, Adenine (A) is paired to Thymine (T) Cytosine (C ) is paired to Guanine (G) Here adenine residues =1, cytosine residues = 1 A= T A= 1= T=1 C= G C= 1= G=1 there fore total number of nucleotides = A T C G =1 X 4 = 480



Base Pair Wikipedia


Solved Nucleic Acid Structure A Draw The Chemical Struc Chegg Com
A goes with T, and C goes with G In RNA A U C and G are present and they bind together to form complementary base pairs, as T is replaced by U, the pairs are C and G, and A and U A, T, G and CPage 7 of 11 Base pairs Attached to each sugar ring is a nucleotide base, one of the four bases Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T) The first two (A, G) are examples of a purine which contains a six atom ring and five atom ring sharing two atoms The second two (C, T) are examples of a pyrimidine which is composed of a single six atom ringAn unnatural base pair (UBP) is a designed subunit (or nucleobase) of DNA which is created in a laboratory and does not occur in nature DNA sequences have been described which use newly created nucleobases to form a third base pair, in addition to the two base pairs found in nature, AT (adenine – thymine) and GC (guanine – cytosine)


Structure And Paired Orientation Of The Unnatural X Y Base Pair Compared To Natural C G Base Pairing Taken From Romesberg And Coworkers Nature 14 Zone In With Zonzone In With Zon


Q Tbn And9gcq1765hocd7s7cyrrdmznaz75sppdugol1abj1lvrrwv4yu Cle Usqp Cau
A does not pair with G because the two large bases are too big to fit inside the Å circle A TC pair has plenty of room to fit into the Å circle, but the bases are too far apart to be stabilized by hydrogen bonds across the helical axis Only a pairing between a single and a doubleringed base has the proper size to fit into the doubleExamples are Hoogsteen base pairs, which are AT or CG analogues Base pairs often are used to measure the size of an individual gene within a DNA molecule The total number of base pairs is equal to the number of nucleotides in one of the strands (eachA green solvent Quantitative thermodynamic analyses shows that A–T base pairs are more stable than G–C base pairs in the hydrated ionic‐liquid choline dihydrogenphosphate because of specific interactions between DNA bases and choline ions
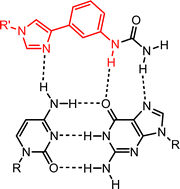


Cg Base Pair Recognition By Substituted Phenylimidazole Nucleosides Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing


Gc Pairs Eterna Wiki Fandom
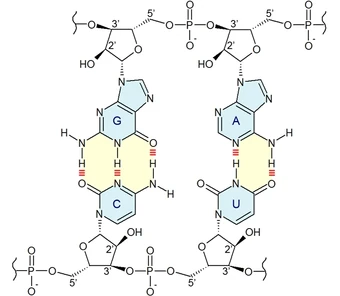
DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helixA goes with T, and C goes with G In RNA A U C and G are present and they bind together to form complementary base pairs, as T is replaced by U, the pairs are C and G, and A and U A, T, G and CSimilarly, in the HDV ribozyme there is a twobasepair pseudoknot mediated via two invariant Watson–Crick G=C pairs between a loop and a singlestranded region Fourthly, the Uturn is a highly recurrent element of RNA structure and is of great importance in folding (eg, two occurrences in the tRNA structure and almost one occurence in any large structure)



h 311 Flashcards Quizlet



Hoogsteen Base Pair An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The first cytosine base editor (CBE), which chemically converts a cytosine–guanine (C–G) base pair into a thymine–adenine (T–A) base pair at a targeted genomic location, was developed inThe nonWatson–Crick type of base pairing also comprises the base pairs formed by inosine (I) with C, T, or A, purine base pairs A · G(or I), A · A, and G · C, and the reverse Watson–Crick base pair A · T In the reverse Watson–Crick A · T pairing, the T ring is rotated 180° around the N3C6 axis from the normal Watson–Crick pairA T G G C T A C Knowing the base pairing convention of A always pairing with T and G always pairing with C makes the complementary strand of the molecule understood It is this feature of complementary base pairing that insures an exact duplicate of each DNA molecule will be passed to its daughter cells when a cell divides


Q Tbn And9gcsphhfj0j0ihg033hkyhtwkmz1fy8zgemj4ak Kv1obd8 Raubz Usqp Cau


Structure Of Nucleic Acids Bases Sugars And Phosphates Sparknotes
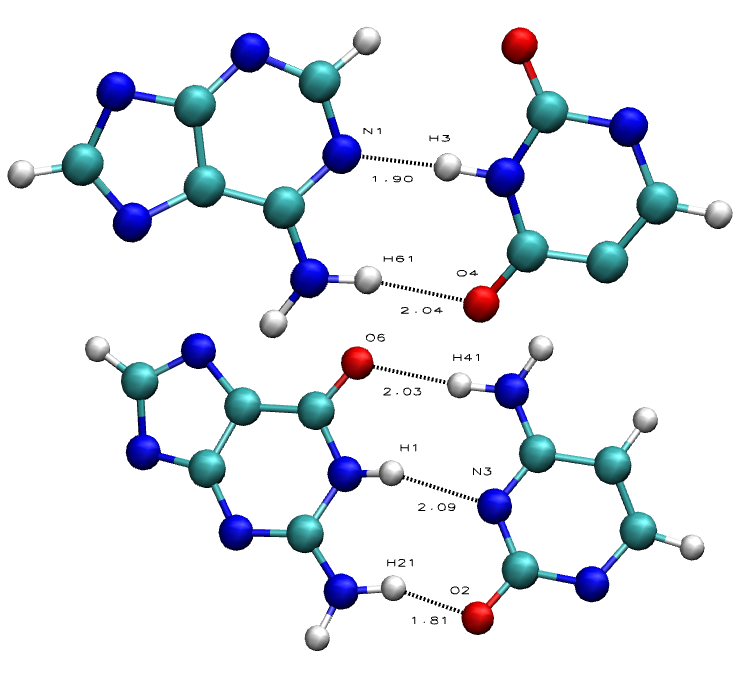
The codon UAU encoded Tyr, but now it is UAG, a stop codon The protein is truncated h) A third mutation occurs which results in the substitution of the C/G base pair at position 42 (shown in bold italics) to a T/A base pairSince the AT pair is held together by 2 hydrogen bonds, and the CG pair is held together by 3 hydrogen bonds, I would think that the CG pairbond is stronger, just like you thought 1In the very stable WatsonCrick G·C base pair, the 2amino group of guanine forms a hydrogen bond with the 2oxygen of cytosine and another hydrogen bond with a surrounding water molecule


Dna Structure



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
Following video illustratres how different edges of Guanine are bonded when involved in either a canonical GC pair, or a socalled sheared GA Glycosidic Bond Orientation A glycosidic bond joins the sugar, ribose, and the base in a nucleotideThe glycosidic bonds of the two bases in a base pair can be oriented in the same (cis) or opposing (trans) directionsWhich base pair bond is stronger in DNA, CG or TA?The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C) Bases on opposite strands pair specifically;


Base Pair
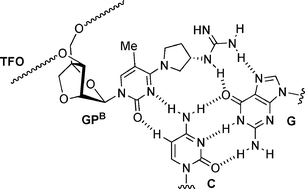


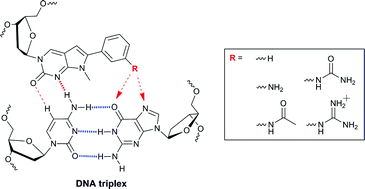
2 4 Bna Bearing A Chiral Guanidinopyrrolidine Containing Nucleobase With Potent Ability To Recognize The Cg Base Pair In A Parallel Motif Dna Triplex Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing
This means that 40% consists of GC base pairs, which would be equally divided between the two bases What would be the sequence of the strand of DNA that is made from the following template 5' GATATCGAT 3' (Your answer must be written 5' > 3')K = G or T = Keto M = A or C = aMino S = G or C = Strong base pair W = A or T = Weak base pair double base codes D = Asp = Aspartic acid E = Glu = Glutamic acid K = Lys = Lysine Q = Gln = Glutamine W = Trp = Tryptophan (big letter big residue) nonobvious codes (you just have to learn them!) B = not A (G or C or T) D = not C (A or G or T) HWith a G/C base pair How would this mutation affect the sequence of the protein that is produced?



How Many Watson Crick Hoogsteen Triple Base Pair Combinations Are There Biology Stack Exchange



Comparison Of Watson Crick Hydrogen Bonding In A Cg Base Pair And Download Scientific Diagram
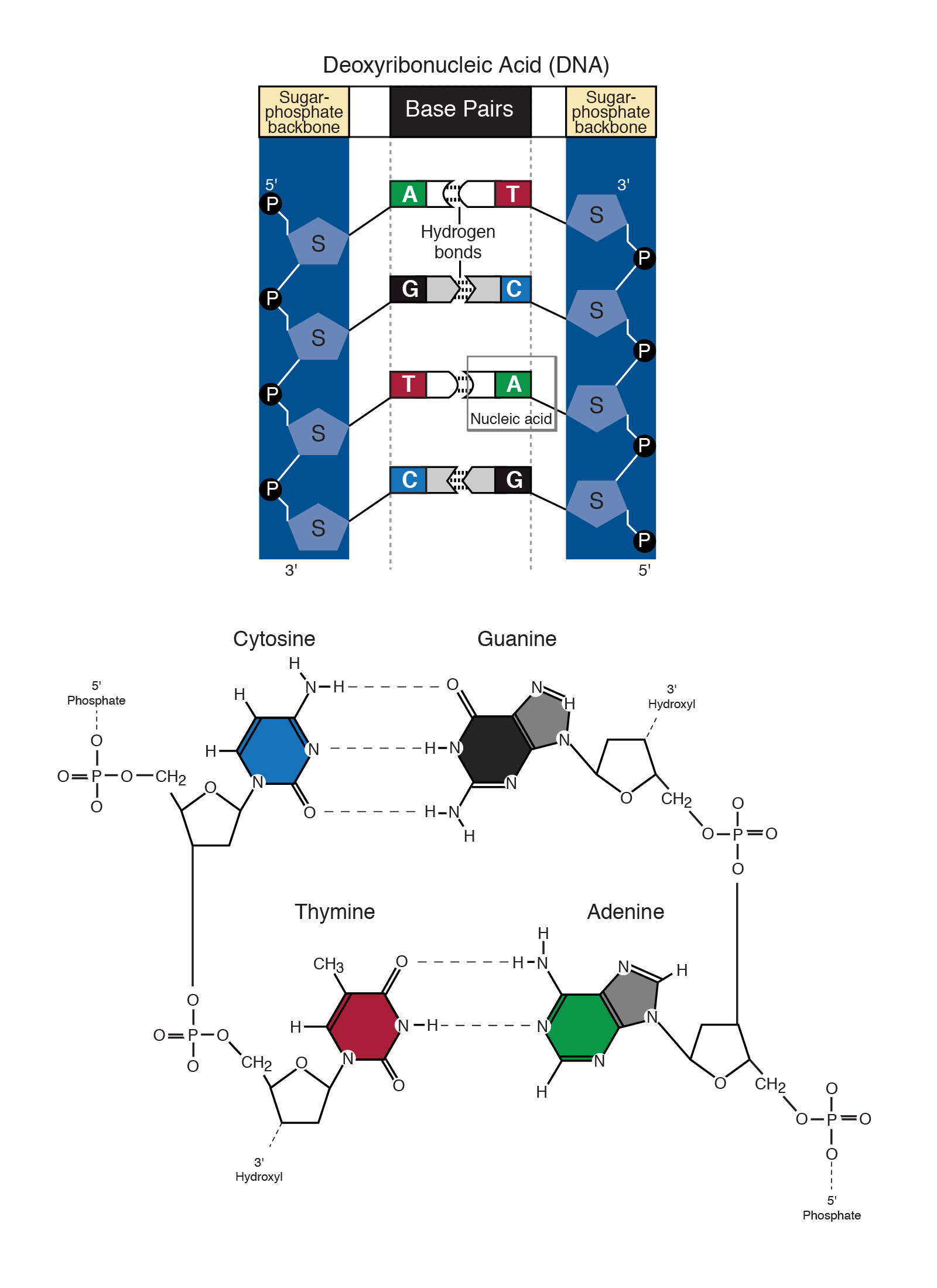
The two base pairs in DNA are the AT base pair and the GC base pair The AT base pair is held together by hydrogen bonds between the A base and the T base Similarly, the GC base pair is held together by hydrogen bonds between the G base and the C base How can we calculate interactions strengths?Incorporating mismatched A/C or G/T base pairs did not noticeably affect the conformations of the duplexes in 115 mM Na but resulted in perturbed BZ conformations at 45 M Na For any mismatched base pair duplex, the BDNA domain of the hybrid BZ structure formed at 45 M Na is significantly perturbed while the ZDNA domain is lessA base pair is two chemical bases bonded to one another forming a "rung of the DNA ladder" The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups Attached to each sugar is one of four basesadenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T)



Stronger Base Pairing Improves Dna Analyses



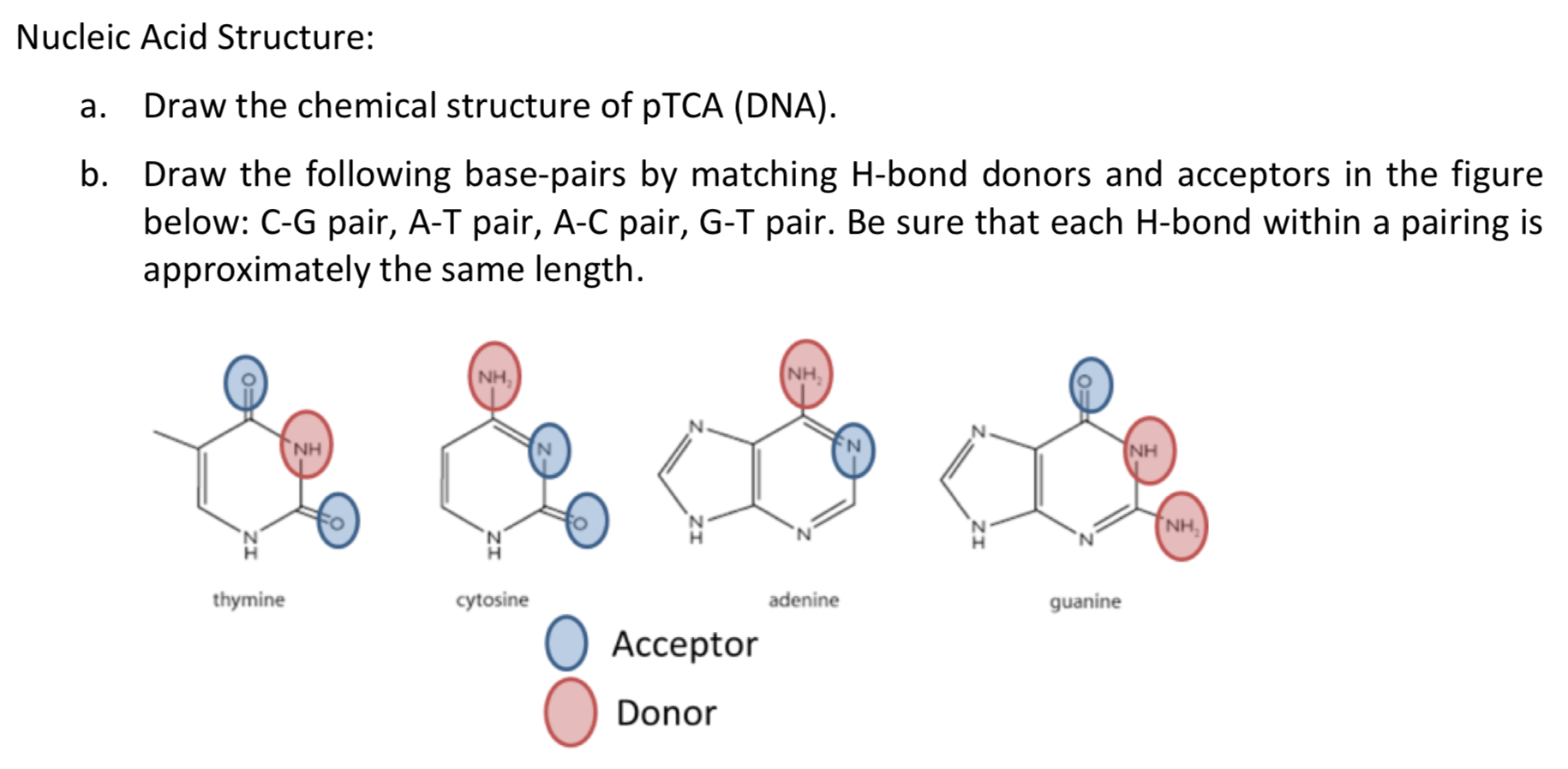
Nucleic Acid Structure
Base editing is the conversion of one target base or base pair into another (eg AT to GC, CG to TA) without requiring the creation and repair of DSBs 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 The base editing is achieved with the help of DNA and RNA base editors that allow the introduction of point mutations at specific sites, in either DNA or RNAAccording to WatsonCrick basepairing, which forms the basis for the helical configuration of doublestranded DNA, DNA contains four bases the two purines adenine (A) and guanine (G) and the two pyrimidines cytosine (C) and thymine (T) Within the DNA molecule, A bonds only with T and C bonds only with G



An Isocytidine Derivative With A 2 Amino 6 Methylpyridine Unit For Selective Recognition Of The Cg Interrupting Site In An Antiparallel Triplex Dna Okamura 14 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library


A T And C G Base Pairs Shakal Blog


Rcsb Pdb 4qz8 Mouse Tdt In Complex With A Dsb Substrate C G Base Pair


Prion



Molecular Interactions Noncovalent Interactions



Rna Secondary Structure Prediction Ppt Video Online Download
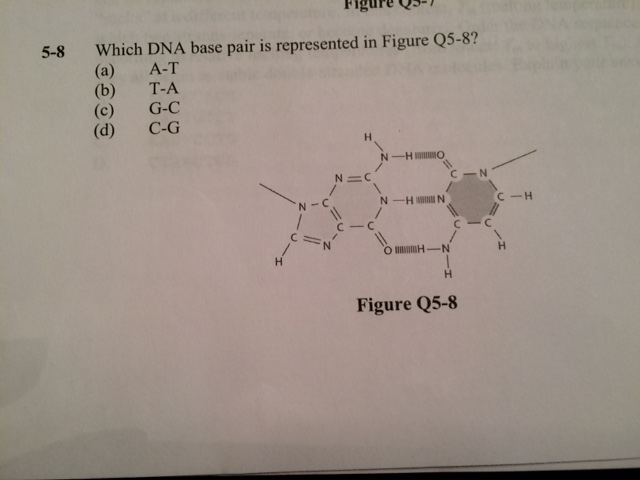


Solved Which Dna Base Pair Is Represented In Figure Q5 8 Chegg Com



Synthesis Of Oligonucleotides Bearing The Non Standard Bases Iso C And Iso G Comparison Of Iso C Iso G C G And U A Base Pair Stabilities In Rna Dna Duplexes Sciencedirect



Triple Stranded Dna Wikiwand



Why Are There Two Hydrogen Bonds Between Adenine And Thymine But Three Hydrogen Bonds Between Cytosine And Guanine Quora


Base Pair Eterna Wiki


Jmol Basepair Demo


Hoogsteen Base Pairing Molecular Biology



Cytosine Guanine Dna Double Helix Base Pair Molecular Model


The Structure Of Dna



Chemical Structures Of Stable Base Triple And Unstable Base Pair Download Scientific Diagram



Structure Function Bioinformatics
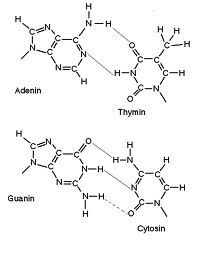


Watson Crick Base Pairing The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki



Figure 1 From Ph Dependent Configurations Of A 5 Chlorouracil Guanine Base Pair Semantic Scholar



Mutations Microbiology


The Structure Of Dna


Glaxo Wellcome And Science Global



Base Pair Wikipedia



Unnatural Nucleosides With Unusual Base Pairing Properties Bergstrom 01 Current Protocols In Nucleic Acid Chemistry Wiley Online Library



Base Pairs Definition Types Biology Class Video Study Com



Molecular Genetics High School Biology Science Khan Academy



Figure 9 19


Biomath Linear Functions Applications



Base Pairs Triplets And Quartets


Biopolymers Problems



Why Do Purines Pair With Pyrimidines Socratic
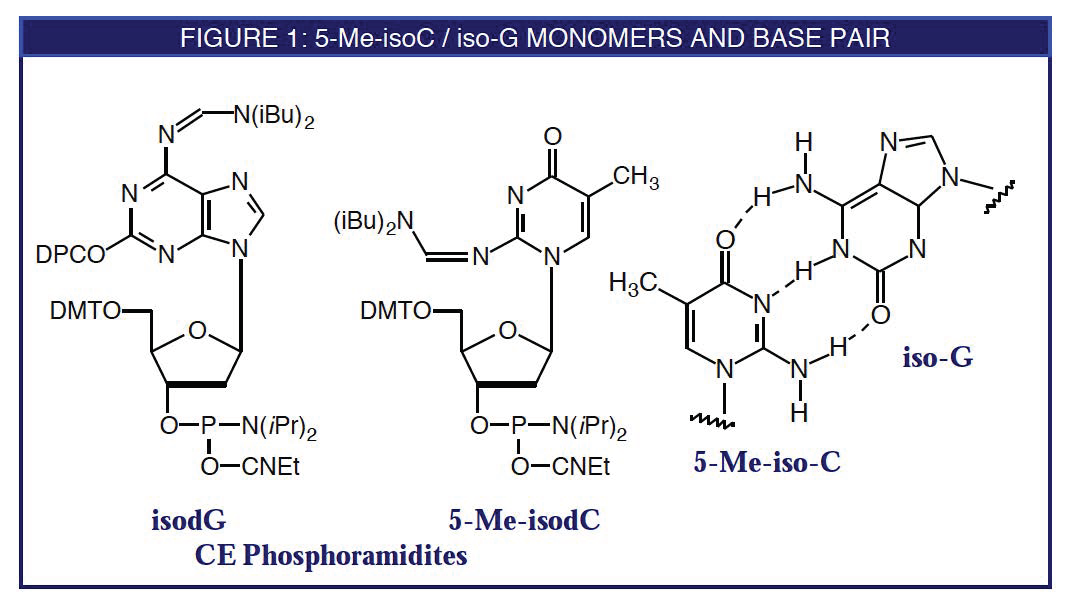


Glen Report 8 12 5 Methyl Isocytidine Isoguanosine Base Pair



Comparison Of Watson Crick Hydrogen Bonding In A Cg Base Pair And Download Scientific Diagram


Base Pair Medical Silver
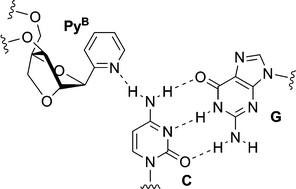


2 4 Bna Bearing A 2 Pyridine Nucleobase For Cg Base Pair Recognition In The Parallel Motif Triplex Dna Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing


Why Do Guanine Pair With Cytosine By Triple Bond And Adenine Pair With Thymine By Double Bond In Any Dna Molecules Quora



Biology Exams 4 U How To Calculate The Percentage Of Bases In A Dna Strand Using Chargaff S Rule Chargaff S Rule Questions


Structure In Chemistry Conformational Analysis Ca13 Problems Problem Ca13 1 Hydrogen Bonding Can Have A Strong Influence On Molecular Shape For Example It Is A Key Factor In Determining The Shape Of Dna In Dna Base Pairs In Adjacent Strands


Q Tbn And9gctvgzgefvpjauhvglwqyckm2jjawwuyxf8vhpqu6mmsfjt Kaib Usqp Cau



Gc Content Wikipedia


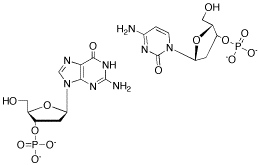
Cg Base Pair Recognition Within Dna Triple Helices By Modified N Methylpyrrolo Dc Nucleosides Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing


Base Pair Wikipedia



File Gc Watson Crick Basepair Png Wikimedia Commons


28 3 Base Pairing In Dna The Watson Crick Model Chemistry Libretexts
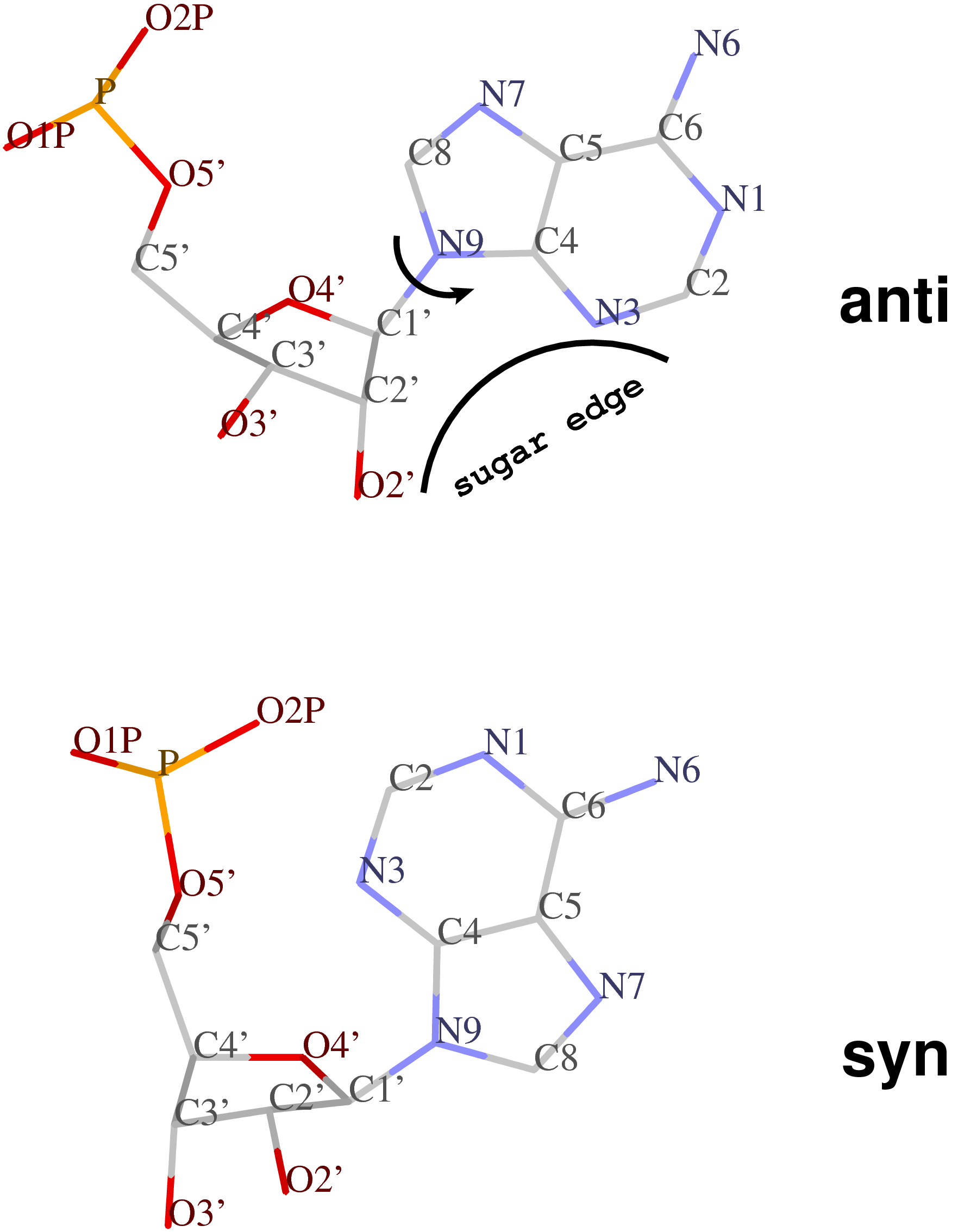


3dna Homepage Nucleic Acid Structures


Nucleotides Composition And Structure



Development And Study Of The Antigene Oligonucleotides Science And Technology Platform Program For Advanced Biological Medicine



Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs


Base Pair Image Swaps



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
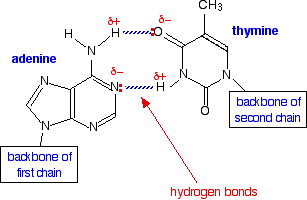


Dna Structure


28 3 Base Pairing In Dna The Watson Crick Model Chemistry Libretexts


How Do Purines Compare To Pyrimidines Socratic
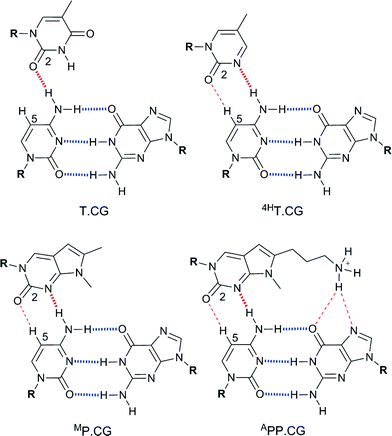


Cg Base Pair Recognition Within Dna Triple Helices By Modified N Methylpyrrolo Dc Nucleosides Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C0obh
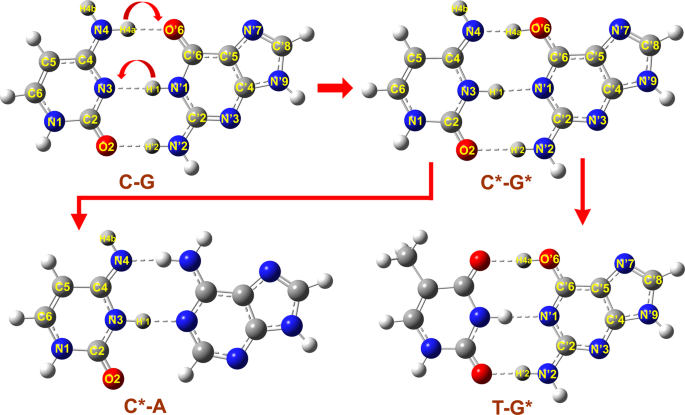


Density Functional Theory Studies On Cytosine Analogues For Inducing Double Proton Transfer With Guanine Scientific Reports



Figure 1 From 5 Methylation Of Cytosine In Cg Cg Base Pair Steps A Physicochemical Mechanism For The Epigenetic Control Of Dna Nanomechanics Semantic Scholar



Capturing The Radical Ion Pair Intermediate In Dna Guanine Oxidation Science Advances


Chargaff S Rules Of Base Pairing



1 Base Pairing And Double Helix Model A Base Pairing Of At And Cg Download Scientific Diagram



Characteristics Of C G And T A Base Pairs Intermolecular H Bonds Download Scientific Diagram



Novel Phthalimide Nucleosides For The Specific Recognition Of A Cg Watson Crick Base Pair Sciencedirect
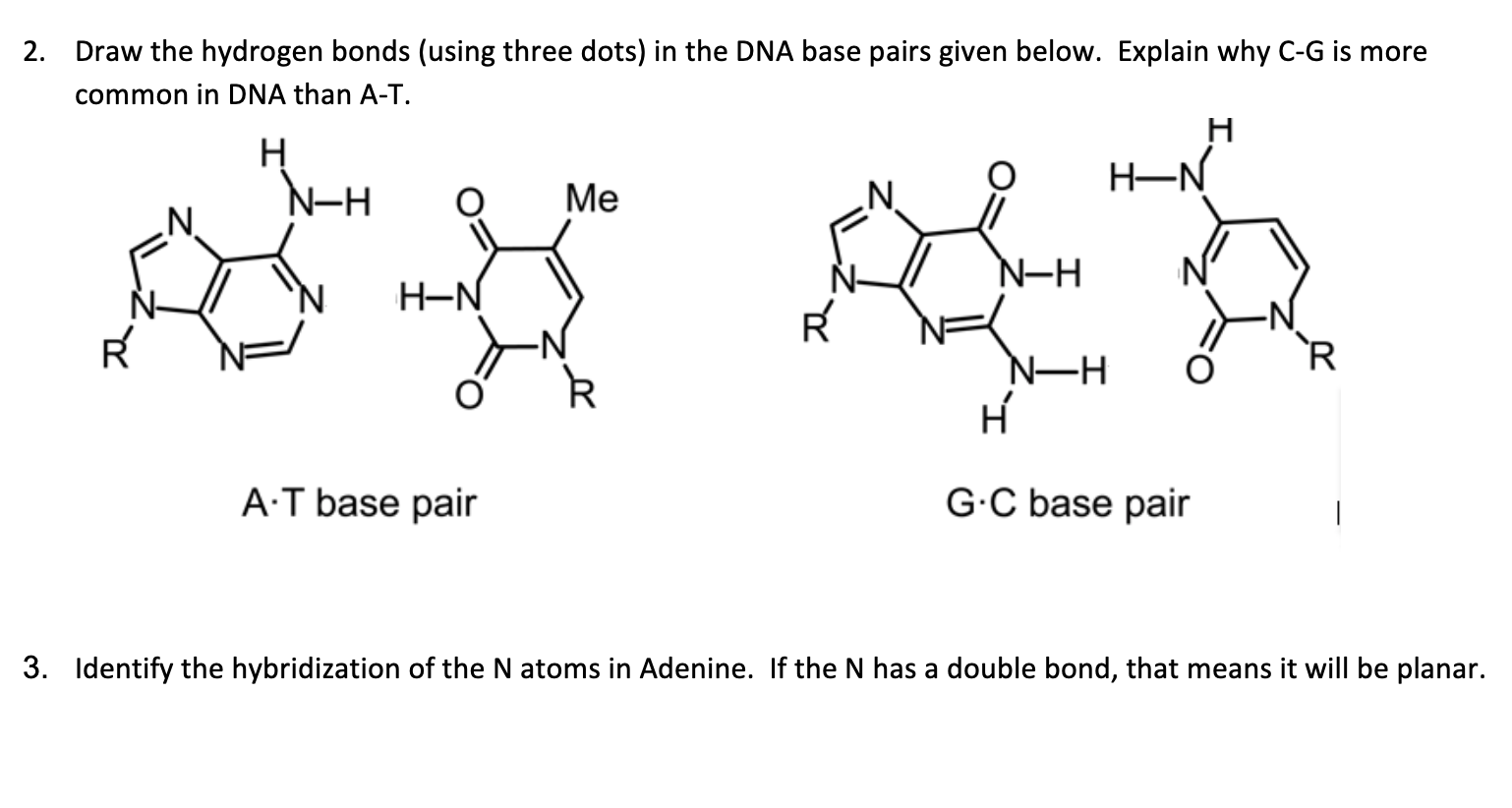


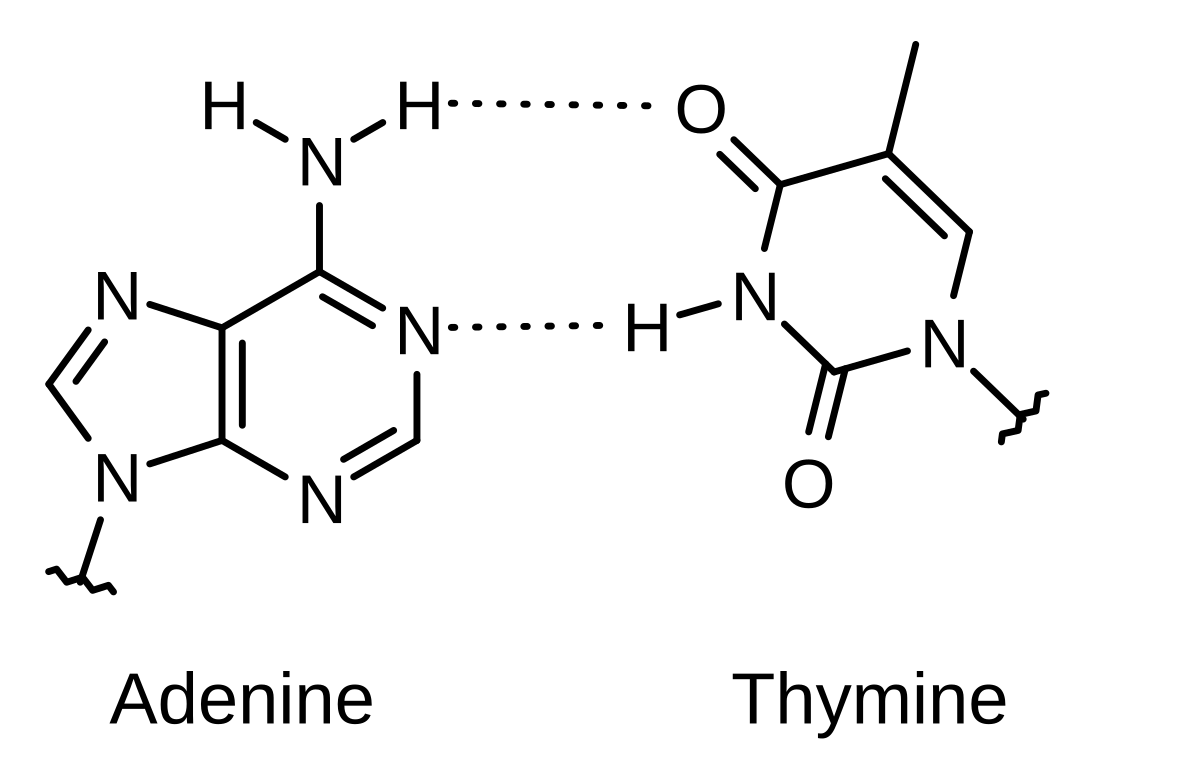
Solved 2 Draw The Hydrogen Bonds Using Three Dots In T Chegg Com


Part a K105 Parts Igem Org


Biopolymers Problems



A T And C G Base Pairs Shakal Blog



Dna Bases And Base Pairs Flashcards Quizlet



A T And C G Base Pairs Shakal Blog


Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs



Selective Recognition Of A C G Base Pair In The Parallel Dna Triple Helical Binding Motif Sciencedirect



Complementarity Molecular Biology Wikipedia



Errors In Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable


Structural Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Dna Dna Structure Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Comparison Between Natural Watson Crick Base Pairs C G T A And The Download Scientific Diagram



Twin Hydroxymethyluracil A Base Pair Steps Define The Binding Site For The Dna Bending Protein Tf1 Journal Of Biological Chemistry


コメント
コメントを投稿